Computer
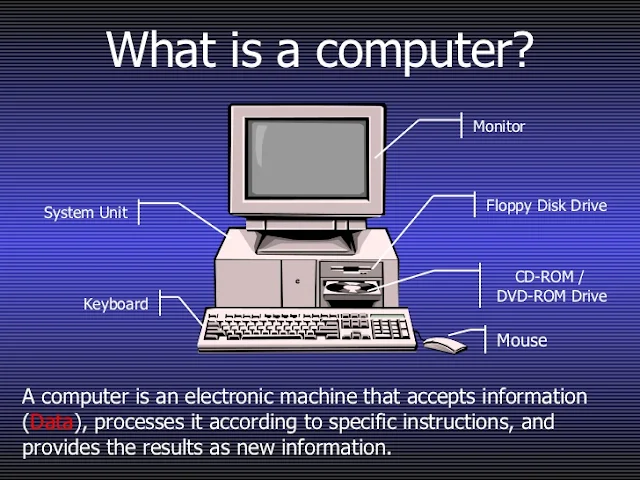
A computer is an electronic device which inputs data processes it and gives result as an output to an output device.Different operations like typing texts, graphic designing , music recording, video and music editing , processing of different kinds of data(like arithmetical, numerical and logical data).Storing photos, videos and other various types of data. It is also used in hospital for diagnosis of disease, in scientific lab for tests and experiment. It is programmable, user will input necessary data like for example there are two number sets (which is as an input from a user from the computer's input device) 5 and 11 there will be a system of instruction for adding the given numbers and also instruction to add is given from an input device by user, then it processes the data and gives the output in its output device as 16.When the first electromechanical computer named as 'MARK-I' was manufactured in 1944 this started the use of electronic computer. About 2400 BC ago Abacus was used to compute arithmetic problems they found easy for addition, subtraction etc, using abacus.Today's electronic computer runs with electricity and has different hardware components and these hardware are run by the help of instruction set which is called as computer program or software.
Did you know that fascinating facts about computers include
that the term "computer" originally referred to humans who performed
calculations? Surprisingly, the first electronic programmable computer, ENIAC,
completed in 1945, could add or subtract 5,000 times per second—a thousand
times faster than any other machine of its era.
The history of computing reveals astonishing origins that
defy our modern perceptions. Before electronic devices took over, the term
"computer" actually referred to *people* who performed calculations
by hand. These human computers, predominantly women during World War II,
meticulously calculated everything from artillery trajectories to astronomical
data with just pencil and paper. One of the most extraordinary pioneers was Ada
Lovelace, daughter of poet Lord Byron. In 1843, while translating an article
about Charles Babbage's Analytical Engine (a machine never actually built), she
went far beyond translation. Lovelace added extensive notes describing the
first algorithm designed to be processed by a machine—essentially creating the
world's first computer program to calculate Bernoulli numbers. Remarkably, she envisioned
capabilities nobody else had imagined, noting the machine could potentially
compose "elaborate and scientific pieces of music" if properly
programmed.
Another fascinating chapter unfolded with ENIAC (Electronic
Numerical Integrator and Computer), completed in 1945 as the . This behemoth
occupied a 1,500-square-foot room, weighed 30 tons, contained 18,000 vacuum
tubes, and cost $400,000. Despite its size, ENIAC could perform calculations at
unprecedented speeds—5,000 additions per second, about a thousand times faster
than previous machines, first general-purpose electronic computer.
Perhaps most surprising of all, ENIAC's first programmers
were six brilliant women: Kathleen McNulty, Betty Snyder, Marlyn Wescoff, Ruth
Lichterman, Jean Jennings, and Frances Bilas. Initially hired as human
computers to calculate artillery tables, these women learned to program ENIAC
despite not even being allowed into the room with the machine during
development due to security restrictions. Their groundbreaking work established
the foundations of modern computer programming, though their contributions went
largely unrecognized for decades.

Comments
Post a Comment